45 energy content of food lab
PDF Caloric Content of Food - Lab Manuals for Ventura College Caloric Content of Food Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: • Read the lab thoroughly. • Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. ... the energy content of the food's chemical bonds. Diet manuals and calorie counter books will, for . 14-2 Lab Answers: Energy from Burning Food | SchoolWorkHelper The least energy as the graph shows is in the Cereal (Koko Crunch). It contains about 1.2 kJ of Average Energy. Candlenut contains the highest amount of energy in the 5 items used during the experiment possessing energy of approximately 8.6kJ. READ: pH Titration Lab Explained
PDF Lab Activity: Measuring Calories in Food - CHRISTINA BOWERS PH.D 9. Attach the temperature probe to the lab-quest mini adapter and connect this to the desk top computer 10. Open "logger pro" and take an initial temperature reading of the water. 11. Measure the mass of your food material and record it in the data table. 12. Now attach the food to the paper clip as shown in Figure 4.

Energy content of food lab
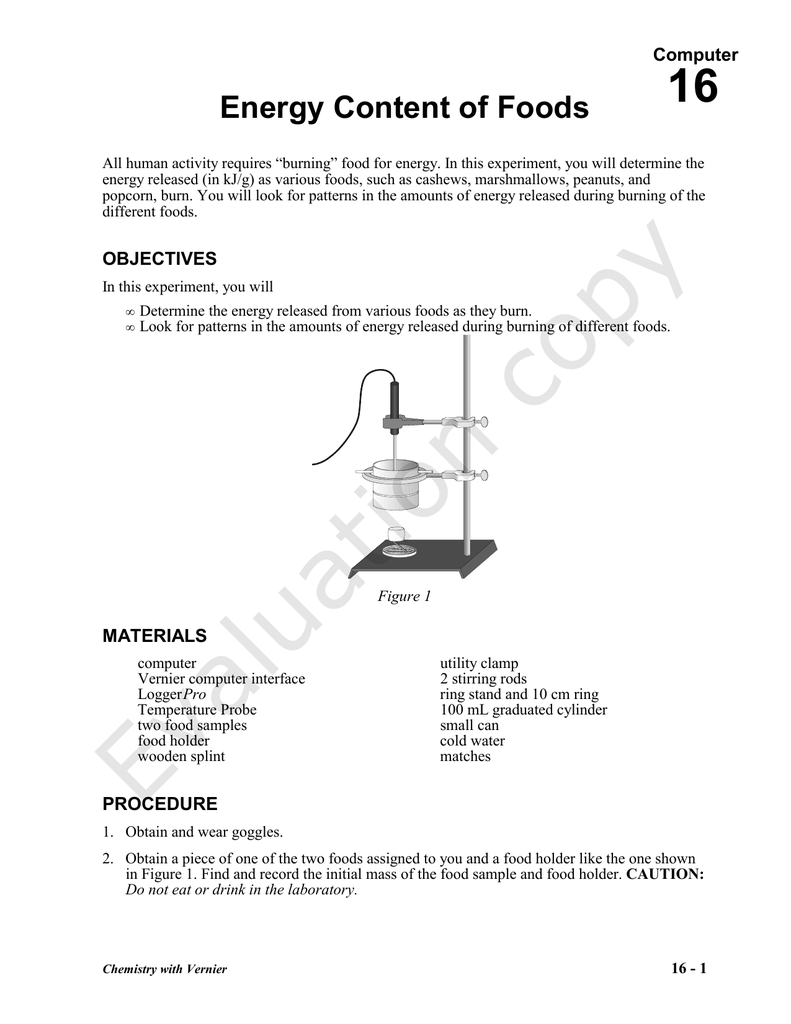
Energy Content of Foods - Vernier All human activity requires "burning" food for energy. In this experiment, you will determine the energy released (in kJ/g) as various foods, such as cashews, marshmallows, peanuts, and popcorn, burn. You will look for patterns in the amounts of energy released during burning of the different foods. Objectives In this experiment, you will PDF Energy Content of Foods - UGA The energy content of foods is investigated. The energy released by a number of food samples and absorbed by water is determined using technology. Inferences about the energy content of foods with high fat content and foods with high carbohydrate content are then made. Hypothesis Foods, depending on their carbohydrate/fat composition, have ... Chapter 3: Calculation of The Energy Content of Foods - Energy ... The value for carbohydrate energy in chocolate is an extreme example - the factors range from 5.56 kJ/g (1.33 kcal/g) to 17 kJ/g (4.0 kcal/g). For most individual foods that are major sources of energy in the diet, use of a specific rather than a general factor results in differences that range from -6 to +3 percent.
Energy content of food lab. Lab Report Caloric Content of Food Purpose - Phdessay 184= 24,455 or 2. cal. Using the following standards (carbohydrates (4 Cal/g), protein (4 Cal/g), and fats 9 Cal/g), determine the caloric content of a bag of your favorite snack food. Chili cheese Fritos Carbs=60 Protein= 8 Fats= 90. Remember: Lab notes are evidence of your work and of your understanding of the concepts demonstrated in the ... Skills Practice Lab Energy Content of Foods - education.ti.com Energy Content of Foods continued 5. Set up the data-collection mode. a. To select MODE, press ¨ once and press e. b. Select TIME GRAPH from the SELECT MODE menu. c.Select CHANGE TIME SETTINGS from the TIME GRAPH SETTINGS menu. d. Enter "6" as the time between samples in seconds. e. Enter "100" as the number of samples. Energy Content of Foods - Vernier Energy content is an important property of food. The energy your body needs for running, talking, and thinking comes from the food you eat. Energy content is the amount of heat produced by the burning of 1 gram of a substance, and is measured in joules per gram (J/g). The energy content of food - Diet - GCSE Biology (Single Science ... When 0.5 g of food is burned, 10 cm3 of water warms up by 20°C. What is the energy content of the food in J/g? Reveal answer. up. down. 1 cm 3 of water has a mass of 1 g. energy transferred to ...
Lab Answers: Energy from Burning Food schoolworkhelper.net/lab-answers ... Measure the energy content in the food item by using the following formula: Results Biscuit Initial Temp After Burn Mass Energy (ᵒC) of Water Temp(ᵒC) (g) Content of Water Biscuit (kJ) Biscuit Trial 1 26 35 0.53 1.426 Trial 2 27 41 0.51 2.305 Trial 3 27 49 0.51 3.696 Koko Initial Temperature of After Burn Temperature Mass (g) of the Koko ... Energy Content of Foods Lab Report - Energy Content of... - Course Hero Energy Content of Foods Introduction: The purpose of the experiment was to determine the energy released (in kJ/g) as various foods, such as cashews, marshmallows, peanuts, and popcorn burn. Patterns will be looked for in the amounts of energy released during burning of the different foods. PDF Title: Energy Content of Foods - Chandler Unified School District The purpose of this lab was to determine the energy content of different foods. Hypothesis: If different foods are burned, then their energy content can be found, because the energy will be transferred to the water in the calorimeter because of the Law of Conservation of Energy. Materials: • Safety goggles • Food samples • Food holder Investigating The Energy Content Of Food | Biology Practicals To sign up for my 2022 Easter Online Revision Courses visit Learning's Perfect Answer Revision Guides are available at ...
Bio lab report 2015- ENERGY CONTENT IN FOODS - Academia.edu The 4 different By keeping the types of nuts. amount of nuts constant, through each experiment. Dependent variable 1. Energy content By subtracting the of food (change final temperature by in temperature). the initial temperature Controlled variable 1. Amount of 1. By keeping the water. amount of water 2. Energy content in foods | Experiment | RSC Education Try this class experiment to investigate how much energy different foods contain In this practical, students burn a sample of a foodstuff of known mass, heating a known volume of water. From the measured temperature change, students calculate the energy transferred to the water, and hence estimate the energy present per unit mass of food. PDF Lab Report: Energy Content of Food - Chandler Unified School District Lab Report: Energy Content of Food Report Due: January 28th (Monday) Rubric • Attach half sheet rubric as your first page to your lab report • NO RUBRIC = LOSS OF 2 POINTS. 1/18/2013 2 Title Page • You need a separate title page for cover • Include: Title of lab: The Energy Content of Food Energy Content of Foods- Lab Report 2.pdf - Lab 2: Energy... Lab 2: Energy Content of Foods AIM The purpose of this experiment is to investigate which type of food, of the foods being tested today, will release the most energy during complete combustion.
Energy Content of Food Lab Report Answers | SchoolWorkHelper Energy Content of Food Lab… Research question: All organisms have activities, organisms use energy to accomplish activates. Organisms eat food to gain energy, this energy is stored for later use. Since humans are organisms we eat food to gain energy. Which food of the same category gives us more energy?
PDF Energy in a Peanut LAB - Mr. Macha's Class Website Energy in a Peanut LAB LEARNING GOAL: Determine the stored (potential) ... released energy is measured in calories and is dependent upon the original energy content of the reactant bonds. Foods that are high in calories have chemical bonds that when rearranged give off large amounts of energy. When a high-energy bond is broken, a large amount ...
Energy Content of Food - Essential Biology Teacher Lab Manual Energy Content of Food Students use a wireless temperature link and a fast response temperature probe to compare the amount of energy available from different food sources. Supports NGSS Disciplinary Core Idea LS1.C Preview Download Student Files Teacher Files Sign In to your PASCO account to access teacher files and sample data. Featured Equipment
Energy Content of Fuels Investigation Lab Report | Studymode 05/14/2013 7.1 Lab Report- Caloric Content of Food TITLE: LAB 7.1 CALORIC CONTENT OF FOOD PURPOSE: In this lab we will have the opportunity to measure the energy in a variety of foods, by heating/burning a portion of the food item and catching the heat released into a known mass of water in a calorimeter.
Energy in Food Lab Presentation by Jessica Ryder The energy content of food can be determined by burning a portion of it and capturing the heat released to a known amount of water. This technique is called calorimetry. The energy content of the food is the amount of heat produced by the combustion of 1 gram of a substance, measured in kilojoules per gram (kJ/g). Ring stand with 2 clamps attached
Energy Content of Food - Agricultural Science Lab Manual | PASCO Energy Content of Food In this lab, students will build a calorimeter to measure the energy content of foods containing dominant macromolecules (carbohydrates vs. lipids). Then, they'll relate their results to energy storage. Source: Agricultural Science Lab Manual Preview Download Student Files Teacher Files
Practical 1.3 - Investigate the energy content of food A simple investigation can be conducted to investigate the energy content of a food sample. Procedure. Add water - around 20cm 3 - to a boiling tube clamped in a retort stand.
PDF Calorimetry: Measuring the Energy in Foods - Carolina.com Never eat or drink in lab. Teacher Preparation and Disposal To reduce student setup time, put 2 rings on each support stand. Place a smaller ring (to suspend the thermometer) above a larger ... Calculate the energy content of the food in kilocalories/gram. 1.65 kcal/1.5 g = 1.1 kcal/g 6. Using information on the nutrition label of the food ...
Energy Content of Food - YouTube In this experiment we measure the temperature change in a can of water to determine the energy content of the food being burned below it and discuss ways this topic can be integrated into your...
PDF Measuring the Energy Content of Food: A Relevant First Law Experiment ... this is achieved by burning the sample in a combustion bomb, measuring the temperature rise of the water in the calorimeter, applyi ng conservation of energy principles to estimate the energy value of the food sample in calories/gram, and comparing this energy value to values obtained from nutriti onal information of a number of potential food …
Chapter 3: Calculation of The Energy Content of Foods - Energy ... The value for carbohydrate energy in chocolate is an extreme example - the factors range from 5.56 kJ/g (1.33 kcal/g) to 17 kJ/g (4.0 kcal/g). For most individual foods that are major sources of energy in the diet, use of a specific rather than a general factor results in differences that range from -6 to +3 percent.
PDF Energy Content of Foods - UGA The energy content of foods is investigated. The energy released by a number of food samples and absorbed by water is determined using technology. Inferences about the energy content of foods with high fat content and foods with high carbohydrate content are then made. Hypothesis Foods, depending on their carbohydrate/fat composition, have ...
Energy Content of Foods - Vernier All human activity requires "burning" food for energy. In this experiment, you will determine the energy released (in kJ/g) as various foods, such as cashews, marshmallows, peanuts, and popcorn, burn. You will look for patterns in the amounts of energy released during burning of the different foods. Objectives In this experiment, you will






0 Response to "45 energy content of food lab"
Post a Comment