39 how does temperature affect viscosity
Viscosity - Chemistry LibreTexts The viscometer is then put into a water bath which equilibrates the temperature of the test liquid. As noted before, the equilibration is important to maintain a constant temperature as to not affect the viscosity otherwise. The liquid is then drawn through the side 2 of the U-tube by use of suction and lastly, the flow is time between marks C ... Relation Between Viscosity And Density - At BYJU'S There is no direct relation between viscosity and density. However, both viscosity and density are affected by temperature. This implies, that for any given fluid, when the temperature is raised, the particles in it start to move apart, bringing down fluid density thereby the value of viscosity also falls down or fluid becomes less viscous. In ...
How Does Changing the Temperature Affect the Viscosity & Surface ... As the temperature rises, liquids lose viscosity and decrease their surface tension — essentially, becoming more "runny" than they would be at cooler temps. What is Viscosity? Viscosity is determined by the time it takes a given amount of liquid to flow through an instrument called a viscometer tube; essentially a narrow pipe.
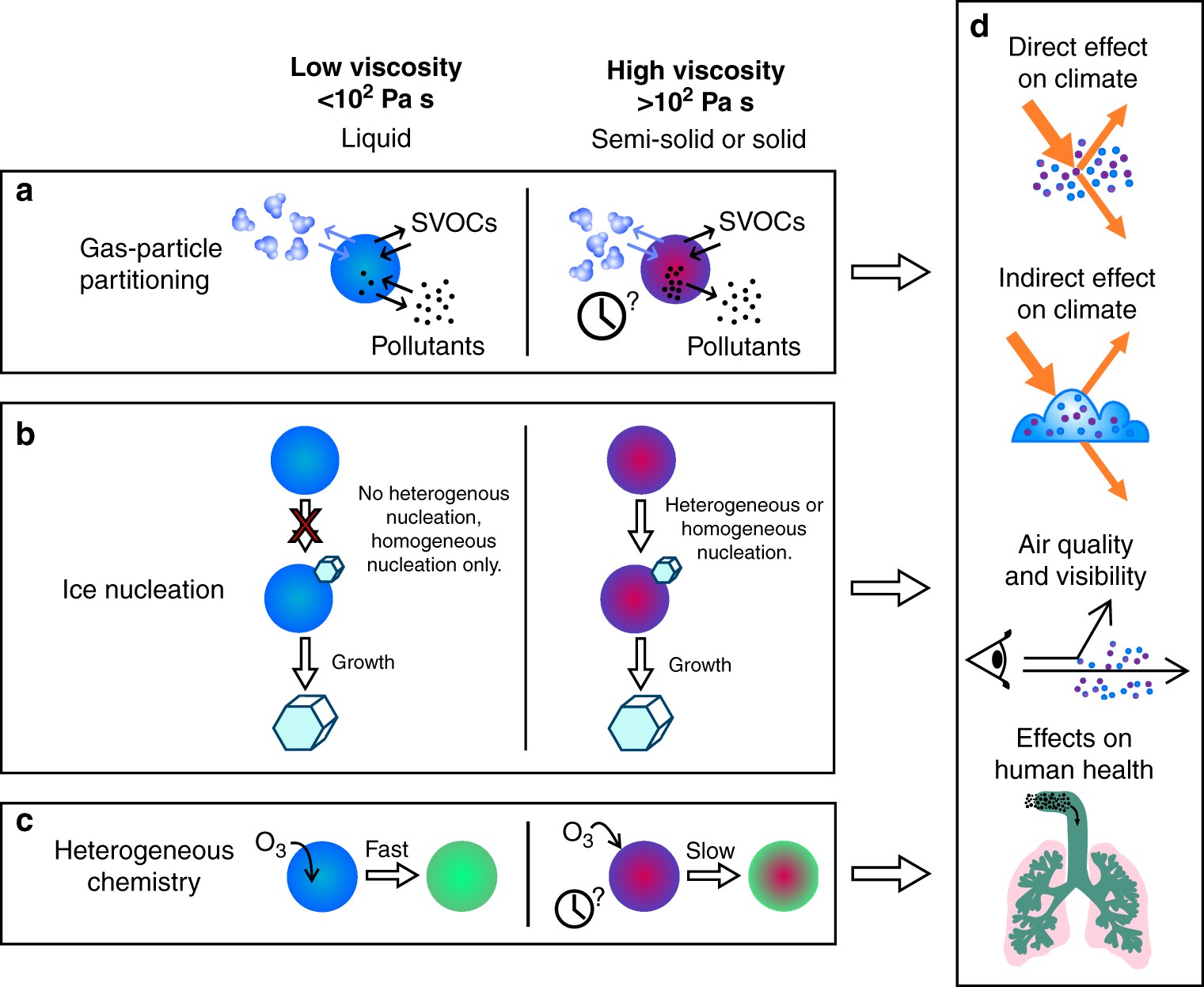
How does temperature affect viscosity
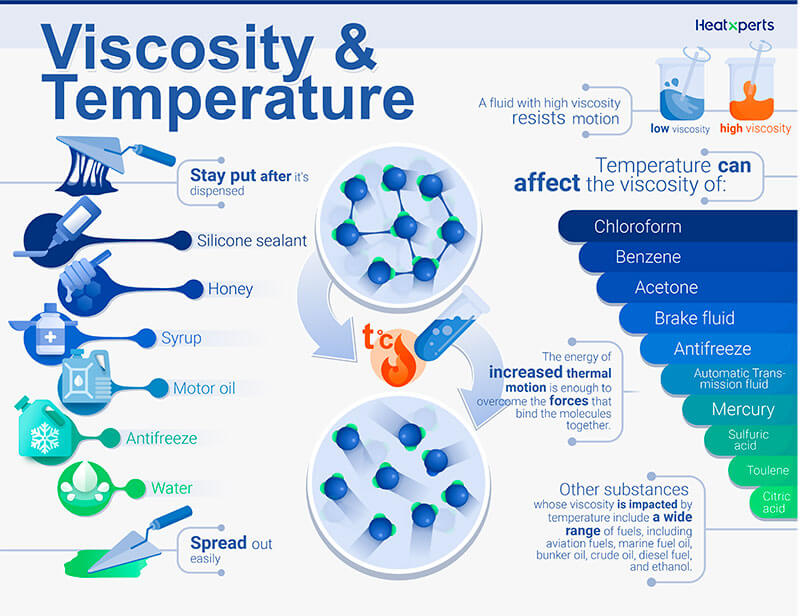
Temperature dependence of viscosity - Wikipedia Increasing temperature results in a decrease in viscosity because a larger temperature means particles have greater thermal energy and are more easily able to overcome the attractive forces binding them together. An everyday example of this viscosity decrease is cooking oil moving more fluidly in a hot frying pan than in a cold one. Gases [ edit] Viscosity - Purdue University The resistance of a liquid to flow is called its viscosity. Viscous liquids like syrup and shampoo flow slowly. Less viscous liquids like water and gasoline flow quickly. The viscosity of a liquid usually depends on its temperature. Viscosity generally decreases as the temperature increases. Viscosity generally increases as the temperature ... Viscosity | Definition, Facts, Formula, Units, & Examples The viscosity of liquids decreases rapidly with an increase in temperature, and the viscosity of gases increases with an increase in temperature. Thus, upon heating, liquids flow more easily, whereas gases flow more sluggishly.
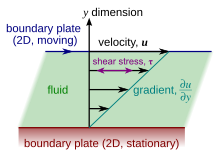
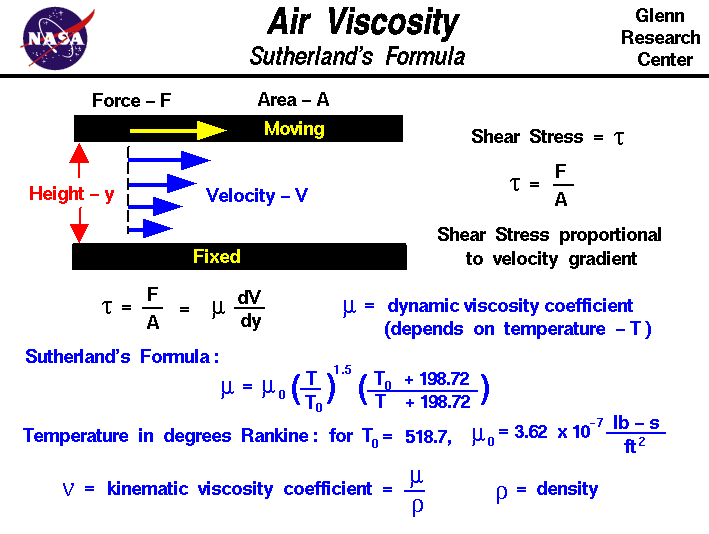
How does temperature affect viscosity. Viscosity - The Physics Hypertextbook Viscosity is first and foremost a function of material. The viscosity of water at 20 °C is 1.0020 millipascal seconds (which is conveniently close to one by coincidence alone). Most ordinary liquids have viscosities on the order of 1 to 1000 mPa s, while gases have viscosities on the order of 1 to 10 μPa s. EFFECT OF pH AND TEMPERATURE ON THE VISCOSITY OF TEXTURIZED AND ... 1000 rpm for 1 h at room temperature. After overnight storage at 4 C, the sample was stirred for another 1 h and heated to the desired temperature. The pH adjustment was per-formed at the temperature intended for viscosity measurement. The remaining deionized water was added to the solution to dilute it to a 10% (w/w) protein solution. 10.7: Viscosity - Chemistry LibreTexts The viscosity of a liquid always decreases as temperature increases. As the molecules acquire more energy, they can escape from their mutual traction more readily. Long-chain molecules can also wriggle around more freely at a higher temperature and hence disentangle more quickly. The Importance of Temperature and Viscosity - RheoSense Viscosity will decrease with increased temperature because as particles move more quickly, they interact for shorter time (shorter interactions) reducing internal friction or stress and therefore decreasing viscosity. Temperature also influences interactions of particles.
How Does Temperature Affect Viscosity? - Reference.com The viscosity of a liquid decreases as the temperature is raised, while the viscosity of a gas increases as the temperature is raised. In a liquid, the increased temperature causes the molecules to move faster, which means that they spend less time pressing against each other and holding each other down. How Does Temperature Affect Viscosity Science Fair How does temperature affect the viscosity of fluids physics? As temperature rises, the attractive forces between molecules weaken, and the molecules are freer to move. Oppositely, if the temperature decreases, then the molecules slow down, and the liquid becomes more viscous. How does temperature affect viscosity of magma? How does temperature affect the viscosity of a liquid experiment? How does temperature affect viscosity and density? In general, liquids tend to get "thinner" when their temperature increases. For example, honey and oil tend to flow better at higher temperatures. Therefore, increasing temperature decreases viscosity. Therefore, increasing temperature decreases density. 9.6: Magma Composition and Viscosity - Geosciences LibreTexts A large amount of linked silica tetrahedra will result in magma or lava that is very viscous, meaning that it cannot flow easily ( viscosity means resistance to flow). The temperature of lava also affects the viscosity; think of how ketchup from your refrigerator flows and how ketchup stored in your pantry flows; of these two fluids, the colder ...
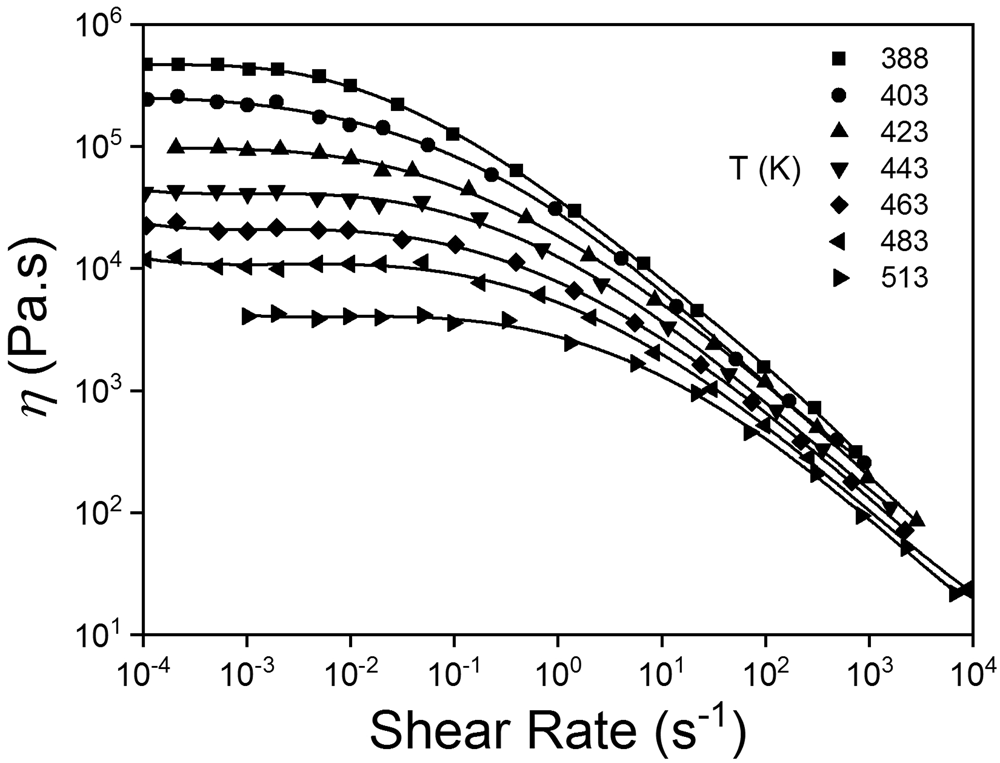
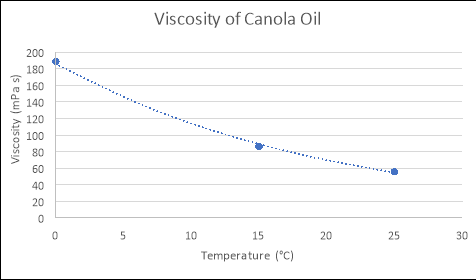
How does Temperature Change Viscosity in Liquids and Gases? - AZoM.com Temperature influences the viscosity of liquids and gases, which is a key parameter in the design of many products such as oils, lubricants, food, and cosmetics. Increasing molecular interchange decreases the viscosity of a fluid as temperature increases and vice versa as temperature decreases. Liquid Viscosity - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The liquid viscosity is highly affected by the heat. The viscosity decreases with an increase in temperature. Most liquids suffer the exponential relationship (Seeton, 2006) between temperature and viscosity rather than linear form (Fig. 6.1).The more viscous the fluid, the more sensitive it is to the temperature change. Variation of Viscosity of Fluid: Effects of Temperature, Formula and ... As the temperature increases the molecular agitation increases i.e., there will be large momentum transfer and hence the viscosity increases. Holman gave the following expression for the viscosity of a gas- Concept of Dynamic Viscosity as a Modulus: We know in a solid body a shear stress is produced against a shear strain. Effect of Temperature on the Viscosity of Honey - Taylor & Francis Influence of temperature on the viscosity of honeys was analysed in the present work. The viscosity value decreased with the increase of temperature. The effect caused by temperature in the range studied was more important in the low range of temperature, whereas at high temperature, the viscosity showed less variation.
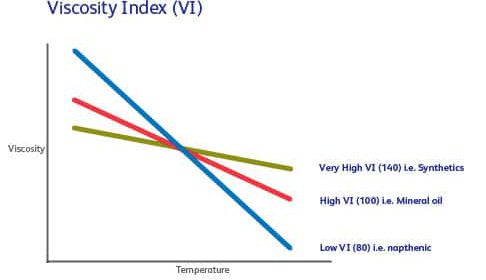
The Effect of Temperature on Lubricant Viscosity - Shell A lubricant's viscosity will change with changes in temperature. As lubricants get hot, their viscosity drops; as they get cold, their viscosity increases. A viscosity index (VI) is assigned to a specific lubricant so that users have a clear understanding of the viscosity state at varying temperatures.
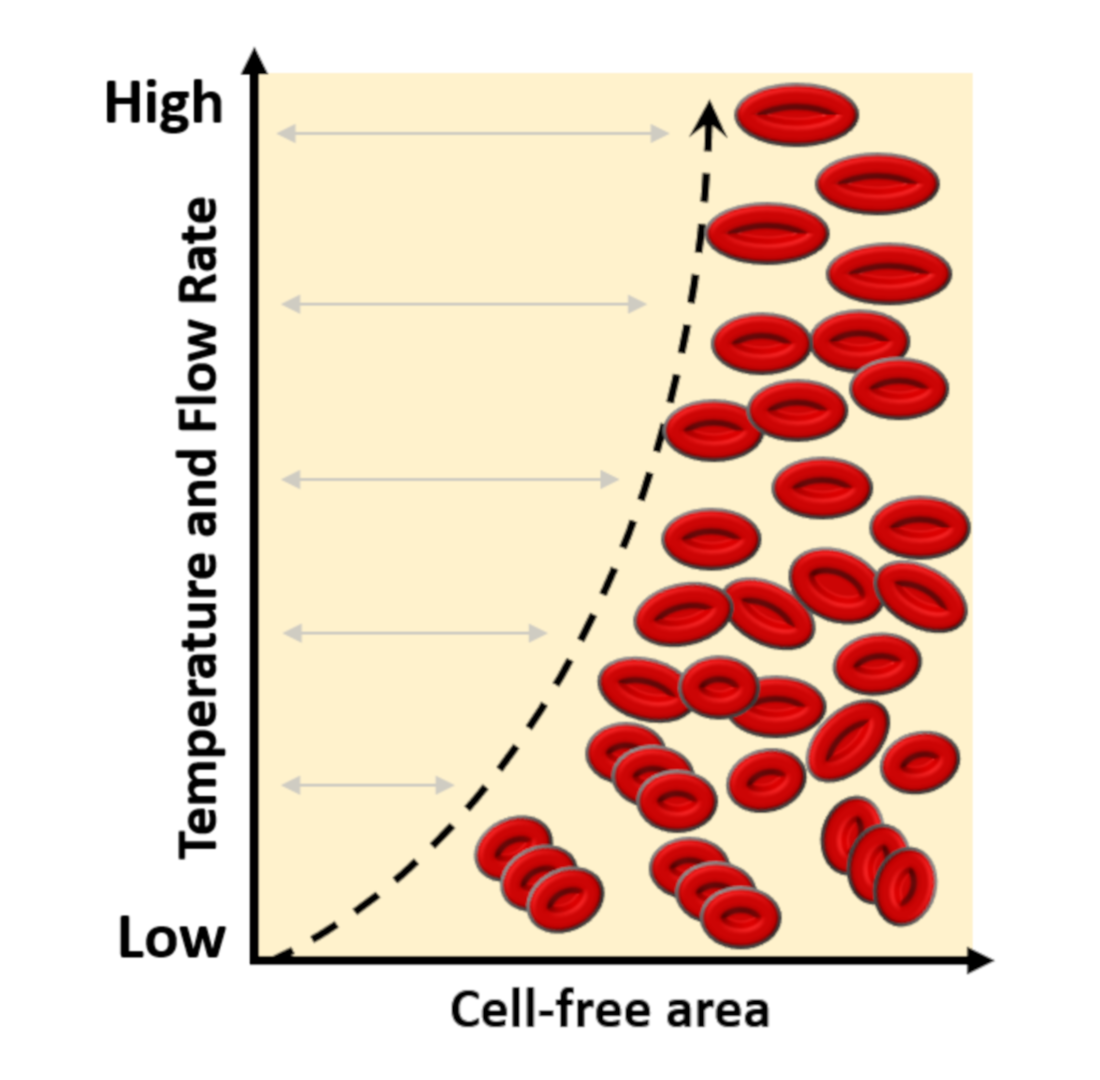
Blood viscosity and blood pressure: role of temperature and ... Effect of temperature on blood viscosity. When blood temperature decreases from 36.5° to 22°C, blood viscosity increases 26.13%. If temperature increases from 36.5° to 39.5°C, blood viscosity decreases 10.38%. To make a more accurate presentation in the graphic representation and statistics, instead of the "relative viscosity" value ...
How does the temperature of a liquid affect viscosity in mathematical ... I know of a viscosity coefficient. Is this something that is inherent to a liquid or is it variable and changes in response to other factors, namely temperature. Is viscosity measured by the viscosity coefficient? Secondly, how does the temperature affect viscosity? Does it alter the coefficient or is it a separate factor that affects viscosity?
Viscosity | Definition, Facts, Formula, Units, & Examples The viscosity of liquids decreases rapidly with an increase in temperature, and the viscosity of gases increases with an increase in temperature. Thus, upon heating, liquids flow more easily, whereas gases flow more sluggishly.
Viscosity - Purdue University The resistance of a liquid to flow is called its viscosity. Viscous liquids like syrup and shampoo flow slowly. Less viscous liquids like water and gasoline flow quickly. The viscosity of a liquid usually depends on its temperature. Viscosity generally decreases as the temperature increases. Viscosity generally increases as the temperature ...
Temperature dependence of viscosity - Wikipedia Increasing temperature results in a decrease in viscosity because a larger temperature means particles have greater thermal energy and are more easily able to overcome the attractive forces binding them together. An everyday example of this viscosity decrease is cooking oil moving more fluidly in a hot frying pan than in a cold one. Gases [ edit]



























0 Response to "39 how does temperature affect viscosity"
Post a Comment